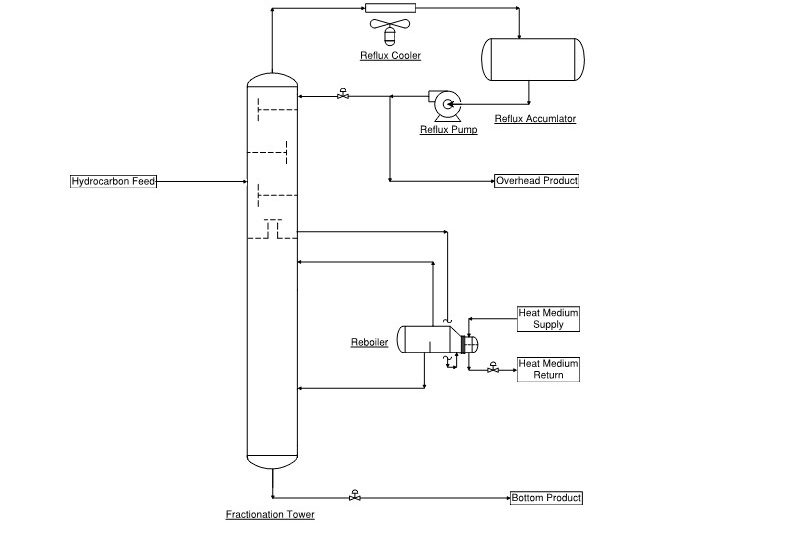
FRACTIONATION DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Internals
• Promotes vapour/liquid contact for component separation
• Evaluate configuration and orientation to avoid issues
Trayed Column
• Suitable to handle lower liquid rates
• Predictable tray efficiency
Packed Column
• Lower pressure drop across tower
• Less susceptible to foaming
Reboiler
• Vapour/liquid separation based on relative volatility
• Heat source and energy recovery
Reflux
• Total or partial reflux to rectify vapours
• Correlation between number of stages and reflux ratio
Products
• Component recovery of overhead and bottom products
• Product purity to meet specification